Pollinators
NC State is committed to protecting pollinators.
Have you heard the buzz? NC State is committed to protecting pollinators. From classrooms to research labs and in landscapes all over campus, NC State helps protect pollinators through research, education, advocacy, habitat and even honeybee hives. These efforts include:
- Pollinator Gardens: These are intentionally landscaped areas that include flowering plants native to North Carolina. To ensure health of pollinators, these areas are not treated with pesticides.
- Pollinator Habitats: While not specifically designed as pollinator gardens, these areas also have important plant resources that are attractive to pollinators and contribute towards a healthy pollinator environment on campus.
- Honeybee Hives: Hives are added to increase the number of beneficial pollinators on campus. Nationwide, pollinator decline over the past several years has accelerated. These managed campus hives boost the health of the campus ecosystem as well as the surrounding environment.
- Academics and Research: NC State has many pollinator-related labs, academic programs and research facilities.
- Student-Led Initiatives: Several student organizations are interested in and have missions related to pollinator maintenance and health, including Entomology Graduate Student Club, Beekeepers Club and Horticulture Club.

Bee Campus USA
NC State is a certified Bee Campus USA affiliate. As part of this initiative, NC State is committed to:
- Maintaining an active Bee Campus USA committee involving staff, faculty, and students
- Enhancing and monitoring pollinator habitat on campus, including increasing the abundance of native plants and providing nesting sites
- Encouraging gardening with locally native plant species
- Reducing the use of pesticides by adopting an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) plan
- Displaying educational signage and host service-learning events
About Pollinators
According to the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation:
- Pollinators are animals, especially insects, that transfer pollen from flower to flower, aiding in reproduction.
- Examples include bats, birds, bees, butterflies, beetles, flies and wasps.
- Bees, with over 20,000 species worldwide, are the most efficient pollinators.
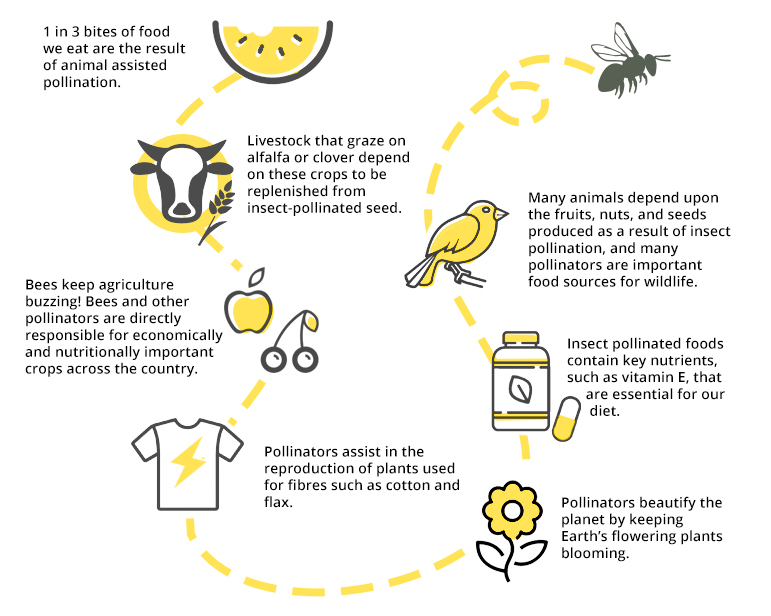
- Pollinators provide vital ecological services. They are responsible for…
- Pollinating over 85% of the world’s flowering plants.
- Pollinating two-thirds of the world’s crop species.
- Contributing to over 30% of the foods and beverages we consume daily.
- Pollinators are at risk of declining populations due to:
- Habitat losses and lack of connectivity
- Pesticide use
- Climate change
- Diseases
- Visit www.Xerces.org for additional information and resources
Pollinator Resources
- The Bees of North Carolina: An Identification Guide
- Bee Campus USA
- NCSU Apiculture Lab
- Campus Sustainability Map
- Bumble Bee Atlas
- Help Map Ground-Nesting Bees
- Creating and Maintaining a Bee Hotel
- Insect Phylogenetic Tree for Insect Identification
- Chatham Mills Pollinator Paradise
- NC State EcoIPM
- Xerces Society
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- Pollinator Partnership
- College of Agriculture & Life Sciences: Preparing students for the important work of food, energy and the environment, CALS is home to numerous academic departments involved in pollinator protection.
- Department of Horticulture Science prepares students to work in the art and science of horticulture. Several courses, professors and graduate students are involved in projects and research on pollinator gardens and vegetable and fruit pollination.
- Department of Agricultural and Human Sciences prepares leaders to extend and teach the knowledge created at NC State. This includes sharing the word about pollinators with all citizens of North Carolina.
- Department of Food, Bioprocessing and Nutrition Sciences works with honey and even uses wasp products to brew beer.
- Department of Entomology and Plant Pathology conducts education and research in the study of insects, including several labs exploring specifically native bees and other pollinators.
- Insect Museum is a research collection dedicated to the acquisition and preservation of insect specimen resources for systematic entomology.
- EcoIPM Lab, led by Dr. Steve Frank, conducts research and extension on urban ecology to support human health, conservation, and recreation in cities.
- Beekeeper Education & Engagement Service (BEES) is an online platform for training beekeepers at all levels.
- College of Design’s Department of Landscape Architecture prepares students for professional careers in landscape architecture and provides education and design services related to ecological landscape design, including landscapes for pollinator protection.
- University Sustainability Office is engaged in promoting and supporting pollinator resources throughout campus.
How You Can Help
